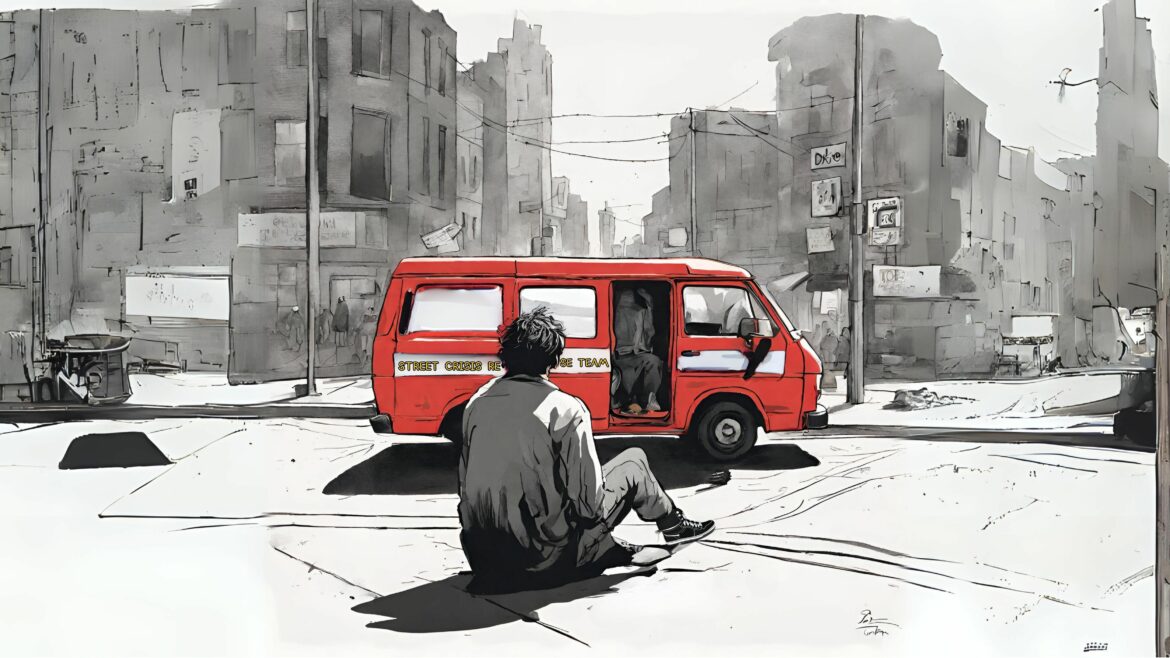
On a windy day last fall, a slender man stood on a corner of the bustling intersection at Van Ness Avenue and Market Street, anxiously seeking help. He flagged us down, asking that we call an ambulance. He said the dead leaves on the ground were out to hurt him and that his legs were bleeding. We didn’t see any blood. He told us his name was Jay and that he was unhoused.
Uncertain what to do, we dialed 311, San Francisco’s non-emergency helpline. Seventeen minutes later, a red van arrived, carrying members of the city’s Street Crisis Response Team. Jay told them he was schizophrenic. The paramedic recognized him from previous calls and greeted him. Looking at Jay’s digital records, a member of the group realized his prescription had been refilled about two weeks prior, but Jay didn’t remember picking it up.
As they spoke, it became clear that Jay had previously been placed under involuntary psychiatric detention, also called a “5150 hold.”
That fall day, Jay asked to be detained again.
[ Read also: “You Report an Unhoused Person in a Mental Health Crisis. This Is What Happens Next” ]
That was how he had gotten a dose of Benadryl, one of two medications he used to manage his condition, he said. Benadryl is among the antihistamines that can help control anxiety. Schizophrenia requires lifelong treatment, even when symptoms have subsided.
“They give me my pill with a 5150,” he said.
The paramedic bristled. “That’s a lot of resources just to get one pill.”
Jay was one of thousands of people last year who fell into San Francisco’s complex, reactive, strained system for treating severe mental health and drug-related crises. As with many of the people who enter that system — including those who are unhoused or are detained without their consent following a call from an alarmed observer — Jay had received temporary care, entailing multiple involuntary psychiatric holds, that failed to address his long-term problems. That left him back on the streets to fend for himself or, with the help of passersby, try again to get the help he needed.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, much of the public discussion about homelessness and mental health in San Francisco has focused on the people who desperately need care, but who reject it. Jay’s story diverges from this common narrative.
“When’s the last time you were at Gen?” the paramedic asked, referring to the emergency room at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center, the facility in the city with the highest number of beds for people on 5150 holds.
“Today,” Jay said. He had gone there seeking medication, then waited in a hallway for four hours before staff gave him a dose of Risperdal, an antipsychotic that he did not usually take. It had not been effective.
Who responds to mental crisis calls
Emergency service providers may not legally turn people away. For many San Franciscans, this is their only option for accessing medical care.
City officials have made recent efforts to improve the crisis care system. A few years ago, police might have been dispatched to Jay’s call and that would divert them from situations they might be better trained to handle. Today, the city routes mental health-related calls to other teams instead when there is not an immediate safety threat, said a spokesperson with the Department of Emergency Management.
One alternative is the Street Crisis Response Team. It was created in late 2020 and aims to offer trauma-informed care to people facing mental health crises or minor medical issues, potentially reducing unnecessary emergency room visits.
When team members arrive on the scene, they address the person’s immediate needs first — for example, food or a warm blanket — and might connect them with other services and take them to a shelter, sobering center or health clinic.
African Americans, despite making up only 6% of the city’s population at the time, accounted for over 42% of people detained four or more times.
The many units that respond to the city’s increasingly visible street-level crises cost millions of tax dollars each year: The Street Crisis Response Team’s budget will be $12.3 million for the fiscal year ending in 2025; the Homeless Outreach Team’s budget for the same year will be $8.9 million; and the Homeless Engagement Assistance Response Team was authorized last year to receive one-time funding of $3 million.
City dispatchers must decide which team to send — they might send more than one — relying on the caller’s description of the scene. Calls about mental health crises often ping-pong between 911 and 311 as details emerge, said Burt Wilson, president of the union chapter that represents San Francisco’s emergency dispatchers.
“It’s a huge amount of resources,” Wilson said.
Involuntary detention’s disproportionate impacts
Dispatchers received at least 24,000 calls about mental health crises or attempted suicides in 2023, including calls from bystanders as well as police, based on a Public Press analysis of government records. In many cases, responders couldn’t find the people in crisis.
In the most serious instances, crisis responders put people in 5150 holds, named after the section of California’s Welfare and Institutions Code that defines this procedure. The law permits police and trained medical personnel to detain someone for up to 72 hours if their mental health disorder is making them a danger to themselves or others, or it leaves them unable to provide for their basic needs.
The city recorded nearly 13,700 psychiatric holds for the year that ended June 2022 — but that figure, the most recent available, captures a fraction of the total situation. The number was calculated in a report by a city working group, which found that not all hospitals reported detentions and that the available data did not allow for robust analyses of patient characteristics like race, gender or housing status.
“There’s a perception that if you put someone on a hold, something good will happen for them, like something miraculous. … That doesn’t really happen.”
Dr. Maria Raven, University of California, San Francisco
Some people were put on 5150 holds multiple times at Zuckerberg hospital. Using data from that facility in its analysis, the working group found that 425 people received at least two psychiatric holds, 86 had at least four holds and 13 had eight or more. African Americans, despite making up only 6% of the city’s population at the time, accounted for over 42% of people detained four or more times.
Most people who received emergency psychiatric services from the hospital, including 5150 holds and voluntary visits, had experienced homelessness in the prior year.
Numerous service providers told the Public Press that people are more likely to cycle repeatedly in and out of crisis-care facilities when they don’t have access to preventive or non-emergency care, because small problems can become larger ones that require hospitalization.
Experts said also that it’s vital for people to receive culturally competent care — for example, when the health worker speaks the patient’s language or knows which medical guidance will conflict least with social norms.
Underfunded care system
San Francisco has seven designated psychiatric facilities with a total of 187 beds for patients on psychiatric holds, according to the California Department of Health Care Services, which approves facilities for this use.
But not everyone on a 5150 hold gets a bed. The crisis care system is notoriously underfunded, with inadequate capacity and staff. When no bed is available, someone is detained in an emergency room for up to 24 hours.
The 2023 passage of state Senate Bill 43 might further strain the system. The law modified the eligibility criteria for 5150 holds for the first time in decades, making it possible to detain people gravely disabled due to substance use. In response, San Francisco has acquired additional beds. Many other counties are waiting to implement the policy, saying they need more guidance and resources from the state to comply.
Meanwhile, Proposition 1, a separate package of state policies that voters approved by a razor-thin margin in March, could add treatment beds to the system, including those for 5150 holds. The proposition forces counties to redirect a large portion of their mental health spending to housing programs, many of which must benefit unhoused people and veterans. A coalition of mental health organizations and disability advocates opposed the ballot measure, fearing it would cause cuts to vital community-based programs.
Among its many mandates, Proposition 1 authorized the sale of $6.4 billion in government bonds. Of the total bond revenue, $4.4 billion is slated to pay for building behavioral health facilities. Gov. Gavin Newsom, who campaigned for Proposition 1’s passage, has said it will enable adding more than 11,150 behavioral treatment beds.
For people who are able to get beds, their problems are far from solved.
“There’s a perception that if you put someone on a hold, something good will happen for them, like something miraculous,” said Dr. Maria Raven, chief of emergency medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. People might think that an intervention by psychiatric workers would set in motion a process that leads to long-term treatment or, for those experiencing homelessness, permanent housing, she said.
“That doesn’t really happen,” Raven said. Instead, “you just put someone where there’s a bed.”
[ Read also: “Mental Health Advocates Call for Voluntary Treatment as Spears Conservatorship Ends” ]
Back on Market Street, the Street Crisis Response Team was trying to find help for Jay in this overburdened system. As they made phone calls to locate a facility that could fill Jay’s medication, one team member tried to comfort him with snacks and water, which he was hesitant to accept.
“Every time I drink something, bad stuff happens,” Jay said.
“You can drink it,” the paramedic told him calmly. “We’re not going to leave you.”
After about 15 minutes and at least four unfruitful calls to multiple agencies, the paramedic suggested that the outreach workers try the Westside Crisis Clinic. They checked its operating hours but found conflicting information online. A call revealed that it was closed for the day.
“It’s very unfortunate that the city runs on banking hours,” another team member said.
Finally, the team found a bed at the Dore Clinic, which provides psychiatric urgent care. Jay could stay there for up to a day. He would have a bed and access to a shower and a phone. That would enable him to call his sister, who could pick him up and help him obtain his medication.
“You can get all your meds tomorrow, something that we can all look forward to,” the paramedic said.
Like many media organizations, the San Francisco Public Press is experimenting with artificial intelligence (A.I.) tools that aid the creation of images for use in some stories. Nearly all our visual content is produced by humans.
The Public Press is part of the Mental Health Parity Collaborative, a group of newsrooms that are covering stories on mental health care access and inequities in the U.S. The partners on this project include The Carter Center, The Center for Public Integrity and newsrooms in select states across the country.
See our related article You Report an Unhoused Person in a Mental Health Crisis. This Is What Happens Next