Climate change is expected to increase the severity and frequency of wildfires and other environmental disasters in California and beyond. Wildfires, like the recent blazes in Canada that brought smoke to the Midwest and Northeast regions of the United States, pose threats to the physical health of older adults, especially those in marginalized communities. Emerging research shows events like these could take a toll on the mental health of older people as well.
After the 2018 Camp Fire tore through Paradise and neighboring areas, claiming at least 85 lives and displacing 50,000 people, some older residents from that region relocated to Carson City, Nev., and nearby locations.
Months later, Dr. Elizabeth Haase, medical director of psychiatry at Carson Tahoe Hospital and Behavioral Health Services and a founding member of the Climate Psychiatry Alliance — a group of mental health professionals raising awareness of the effects of climate change on mental health — said she observed worsening health, including exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and rapid progression of dementia in some of the older people who had relocated from the Camp Fire zone.
“People can have a very dramatic decrease in their overall mental and physical health that’s connected to one of these climate events — that is likely to get missed, in terms of the association,” Haase said. One of her older patients developed pneumonia in addition to worsening of her chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and was hospitalized for several months, she said. Her patient’s mental health also deteriorated.
“In offering her the understanding — because I’m somebody that knows about climate and health — that what was happening to her now is linked to her experience in the fire was actually quite therapeutic for her,” she said. “And you know, a lot of sort of depressive and grief-related symptoms came out. And we were able to talk a little bit about what it means to be in your 70s and lose your home with absolutely no possibility, financially, of rebuilding.”
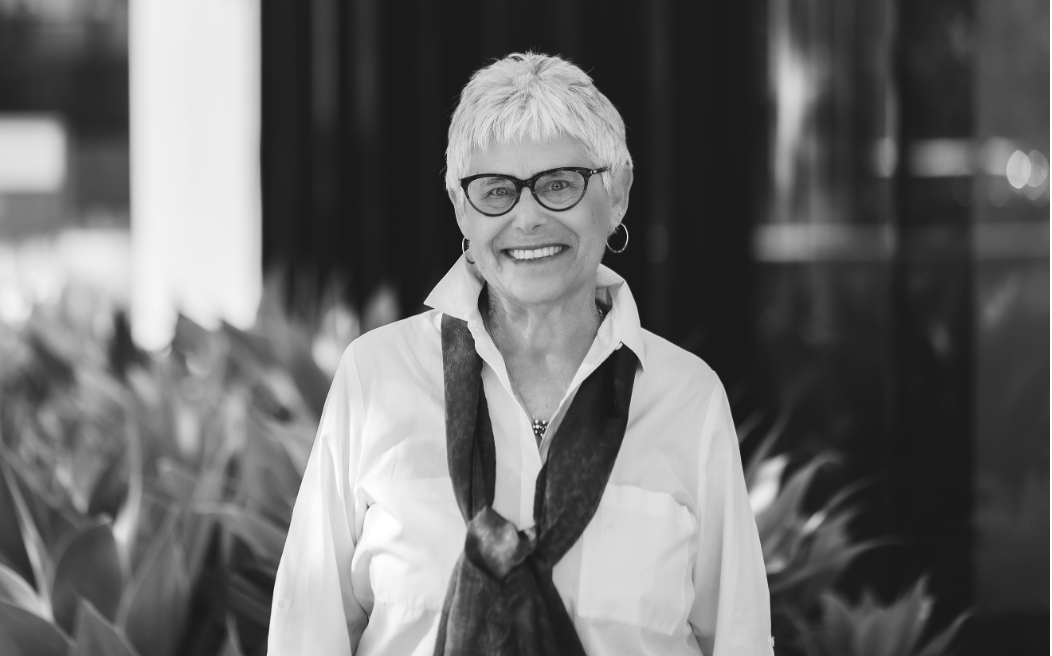
Like Haase, mental health experts based in the San Francisco Bay Area are exploring the ensuing physical, mental and emotional effects of climate change. Dr. Robin Cooper is co-founder and president of the Climate Psychiatry Alliance, and an associate clinical professor at the University of California, San Francisco’s Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences. She also has a small private practice in the city.
Cooper spoke with the San Francisco Public Press about what needs to be done locally to address climate change’s mental health toll. The following excerpts from the interview have been edited for length and clarity.
You’ve been working as a psychiatrist for decades, and in recent years, you’ve been exploring the threats of climate change to mental health. What got you interested in this field?
I have always been, outside of my professional endeavors, an activist. At the time that I began to learn about and think about and be introduced to the issues of climate change, it had that — “Wake up! Oh my God, this is a potential existential threat.” Once knowing about something that profound, I can’t turn myself away from it. And I began to be active in a number of organizations that were addressing climate change in its broader sense. But as I began to discover, I could use my voice most effectively in the realm that’s close to my work. So, I began to be involved much more in the health impacts of climate change.
A lot was being said about the general broad range of health impacts, but at the end of a talk, a pulmonologist or cardiologist or infectious disease person would say, “Oh, by the way, there’s some mental health impacts.” And I was shocked. I said, “Oh my God, we should be talking about that. We need to be the experts on that.” I met other likeminded psychiatrists, but our voice was very, very tiny at that time. And we came together with the idea that this was something we needed to take ownership of, know more about and be able to speak to it.
Could you describe how climate change affects the mental health of older adults?
So, you and I are both Californians, we know about the Paradise fire. Paradise was a community that had a large number of retirees. It was affordable. It was a place where people could go after years of living in other communities, buy a home that was going to be their place of retirement and live up the rest of their lives. The massive loss of their homes, their community, the place that they could live. These are people who retired, they’re on fixed incomes, who lost everything. So, when you lose your home, and you don’t have a lot of economic resources for rebuilding, you really have secondary emotional impacts. And so, where do you live? The loss of your social support — the greater level of poverty that you live out the rest of your life — interferes with the ability to make choices. And that has huge emotional impacts with depression, post-traumatic stress and a greater vulnerability.
If we look at the disasters that happened in Puerto Rico [in 2017 following Hurricanes Irma and Maria], particularly, the elderly were left on their own. They had no access to medications. Young people had gone to the U.S. mainland for jobs. So, the elderly were left on their own with little to help them recover. And those have huge implications for their emotional wellbeing and their physical wellbeing.
As extreme weather events continue to increase, what should local governments, hospitals, nonprofits and other organizations that are providing services to older people be doing now to strengthen the mental health infrastructure?
We’re in a big crisis, as you know, in health care delivery. We need to make changes in our health care delivery as we confront the vast kinds of troubles that people are going to experience from climate change. And that means shifting to funding and providing care in a more public health, community health manner using population-based ways of intervening. It means that the governmental agencies and those who pay for health care have to do that in a different way.
It also means empowering people in communities to do that before there are extreme heat waves and disasters. It means tightening up our neighbor-to-neighbor relationships, particularly for the elderly. That’s incredibly important, because they can be isolated, left alone, not able to care for themselves. If we have a public health model, and a model based on connectivity in communities, we can have partnerships. We can have buddy systems so Joe knows that Mrs. Smith, who is 86 years old and in her home, is alone and knows what she needs, and has someone to bring her to cooling centers, or help modulate continuing her medications as these disasters and climate events emerge.
Let me just give you another little example. Hurricane Sandy hit New York and the Eastern seaboard with ferocious impacts. Elderly people in this particular public housing that I’m aware of were stuck in their apartments for days without food, light or ability to get out because of the elevators not working. And then people came to the door. And they didn’t know if they were safe. They didn’t know if those were intruders who were going to hurt them, or people there to help them. It doesn’t have to be that way if we take care of some of these things before.
UCSF launched a climate change and mental health task force in June 2019. What did the group set out to do and what has it accomplished, especially for older people?
I would say our achievements have been in the realm of educating mental health trainees about the impacts of climate change in mental health. I believe that medical students need to be what we call climate literate in their educational endeavors. How can we train doctors, and anyone in health care, adequately, if we don’t train them to think about the most significant threat to our wellbeing of this century?
That task force is now being integrated more into this campuswide center on climate health and equity, which actually is a UC-wide endeavor that the Office of the President has supported that is multi-campus, although it’s primarily based at UCSF. I will say it is profoundly underfinanced.
Are you aware of other projects like that in the Bay Area?
There are things happening at many institutions, not with creating a task force, but other kinds of things. Stanford has a new faculty position for one person in the Department of Psychiatry to embed climate change and mental health into their department. Davis has a number of people who are exploring and doing research. But I will say to you, all of these things are siloed. Coming together is a really big issue in the realm of climate and mental health.
The surgeon general, Dr. Vivek Murthy, last month sounded the alarm about the loneliness epidemic in the U.S., and how social isolation has a detrimental effect on the health of older people. And climate disasters could worsen this disconnection, especially if older adults are displaced from their homes and communities. So, on a local level, what steps can be taken to alleviate the loneliness crisis?
I think it is enhancing recreational, social meal programs that bring people outside of their homes and engage them with each other in socially involved activities. We know that caregivers are so underpaid, and that there’s been a massive loss in numbers of people who are doing caregiving for the elderly, because you can’t make a living off of it. We have to fund caregivers, so that those who are isolated in their homes have regular connection.
Given all the challenges and complexities of investigating and implementing solutions to address climate change’s toll on mental health, what gives you hope for the future?
Hope is a funny word. Hope is not optimism. Hope is not like, “I can see our way out of this.” We are going to have very, very significant, enduring, unrepairable damage from the impact of climate change. What gives me hope is this new way of defining hope — radical hope. I can envision a better world to live in. And when I see what’s happening, I can’t turn away from it, I have to lean into it. And some people are saying now, hope is a verb we create out of the activism that we do to confront our wicked problem. And what we do now is not going to make this all nice and better, but it will affect the kind of world that we’re moving toward in the future.
This Q&A, part of a series of stories on the health impacts of climate change on older adults, was produced with the support of a journalism fellowship from the Gerontological Society of America, the Journalists Network on Generations and the Archstone Foundation.
See also: